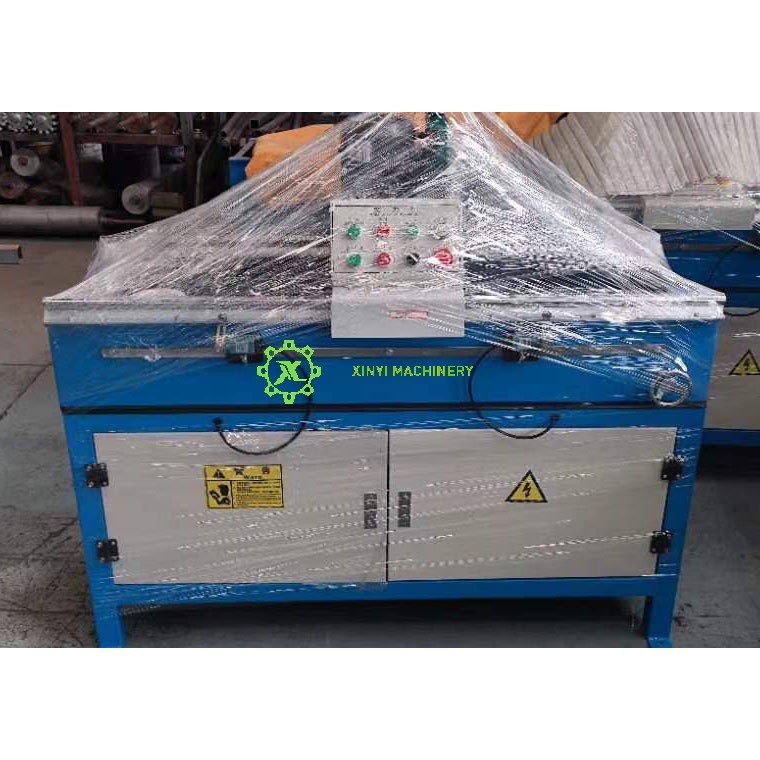
Proper maintenance of plastic crushers is critical for safety, efficiency, and longevity. Follow this structured maintenance protocol to minimize downtime and repair costs:
1. Daily Maintenance
Task | Procedure |
Visual Inspection | Check for loose bolts, cracks in housing, or damaged safety guards. |
Hopper/Chamber Cleanout | Remove plastic residues with brushes/air guns (prevents overheating). |
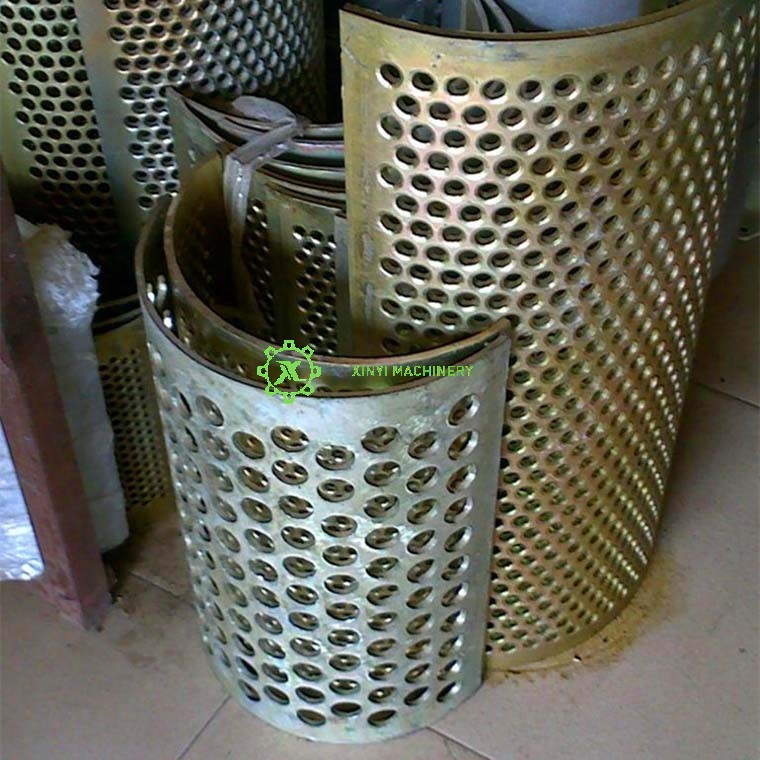
Screen/Grate Clearing | Unclog holes; inspect for wear (>10% hole enlargement = replace). |
Lubrication Spot-Check | Verify grease levels in bearings; listen for grinding noises during operation. |
Dust Management | Vacuum dust from motors, vents, and electrical panels (prevents fires). |
2. Weekly Maintenance
Component | Action |
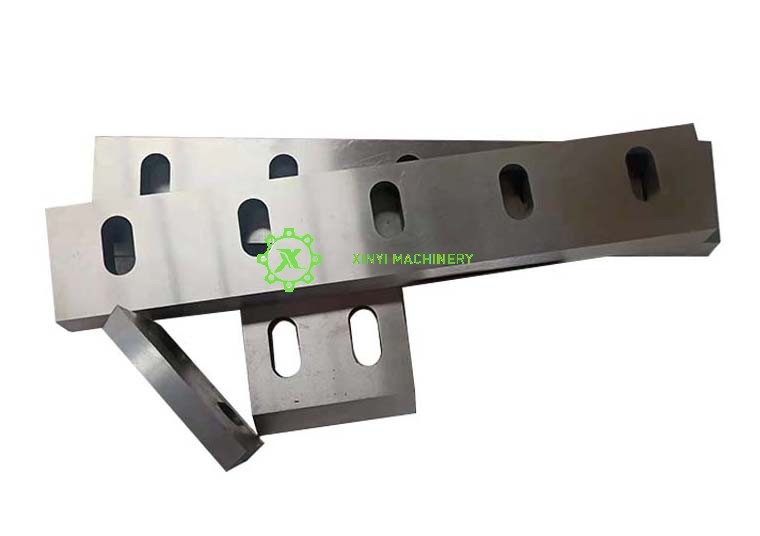
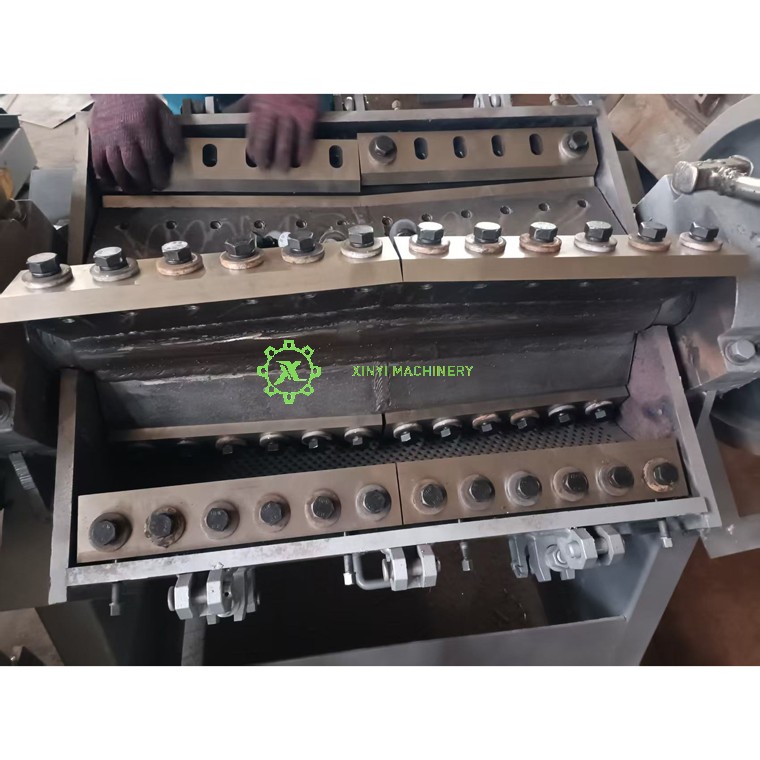
Blades/Knives | Inspect edges for chips/dulling. Rotate or flip blades to distribute wear evenly. |
Bearings | Replenish high-temp grease (e.g., lithium complex). Check temperature: >70°C (158°F) indicates failure. |
Belts/Chains | Adjust tension; misalignment >1mm/m causes premature wear. |
Drive Motor | Clean cooling fins; check amperage draw (overload = 10%+ above rated). |
Hydraulic Systems | Check fluid levels, leaks, and hose integrity (if applicable). |
3. Monthly/Quarterly Maintenance
Task | Key Steps |
Blade Sharpening/Replacement | Sharpen when edge radius >0.2mm. Replace if cracks/chips >3mm deep. Torque bolts to OEM specs (e.g., 90-110 Nm). |
Bearing Replacement | Replace if vibration exceeds 4.5 mm/s RMS. Use sealed bearings with air purge ports for dusty environments. |
Rotor Alignment | Verify rotor balance (misalignment >0.05mm causes vibration). Check shaft runout with dial indicator. |
Electrical Testing | Tighten terminals; test overload relays, contactors, and emergency stops. |
Screen/Grate Replacement | Replace if holes are distorted or cracked. Match hole size to target plastic particle size. |
4. Annual Overhaul
Disassemble crusher fully.
Inspect/replace seals, bushings, and wear plates.
Rebuild rotor assembly (dynamic balancing required).
Rewind/replace motor if insulation resistance <1 MΩ.
Calibrate sensors (temperature, vibration, overload).
5. Critical Best Practices
Safety First
Always LOCKOUT/TAGOUT before maintenance.
Wear cut-resistant gloves and eye protection when handling blades.
Contamination Control:
Use magnetic separators or metal detectors to stop ferrous debris.
Never process PVC (releases hydrochloric acid) or wet/organic materials.
Blade Care:
Store spare blades coated in anti-corrosion oil.
Use good sharpening wheels for sharpening blades.
Moisture Management:
Install desiccant breathers on bearing housings.
Use compressed air (≤0.5 bar) to blow out residual moisture.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Problem | Likely Cause | Fix |
Excessive Vibration | Unbalanced rotor, loose bolts, worn bearings | Rebalance rotor; torque all bolts; replace bearings. |
Overheating Motor | Blocked vents, voltage drop, overloading | Clean cooling paths; check voltage stability; reduce feed rate. |
Jamming | Oversized material, dull blades, caps | Pre-cut large items; sharpen blades; crush bottles with caps attached. |
Reduced Output Size | Worn screens, blade gap too small | Replace screens; adjust blade clearance (0.3–0.5mm for PET, 0.5–1mm for PP caps). |
If you can’t solve problems, you can ask the engineer team of Xinyi Machinery.
(Xinyi Machinery is a China leading Manufacturer of all kinds of plastic crushers.)
Final Advice: Keep a maintenance log with dates, parts replaced, and observations.
Adhere to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule but adjust based on your material mix – caps and reinforced plastics accelerate wear. Partner with your crusher OEM for customized solutions!