Plastic crushers and shredders are both used to break down plastic materials, but they differ in design, function, and application. Here’s a comparison:
1. Crushing Mechanism & Output Size
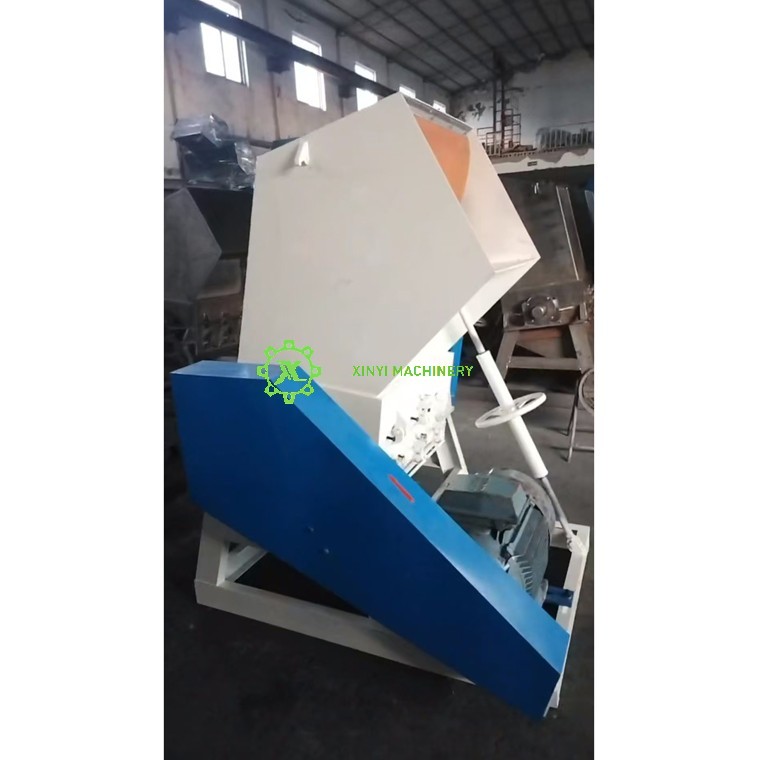
· Plastic Crusher:
o Uses rotating blades or cutters to cut, shear, and crush plastic into small, uniform granules (typically 5–20 mm).
o Suitable for brittle or hard plastics (e.g., PET bottles, HDPE containers).
o Produces clean-cut fragments ideal for recycling.
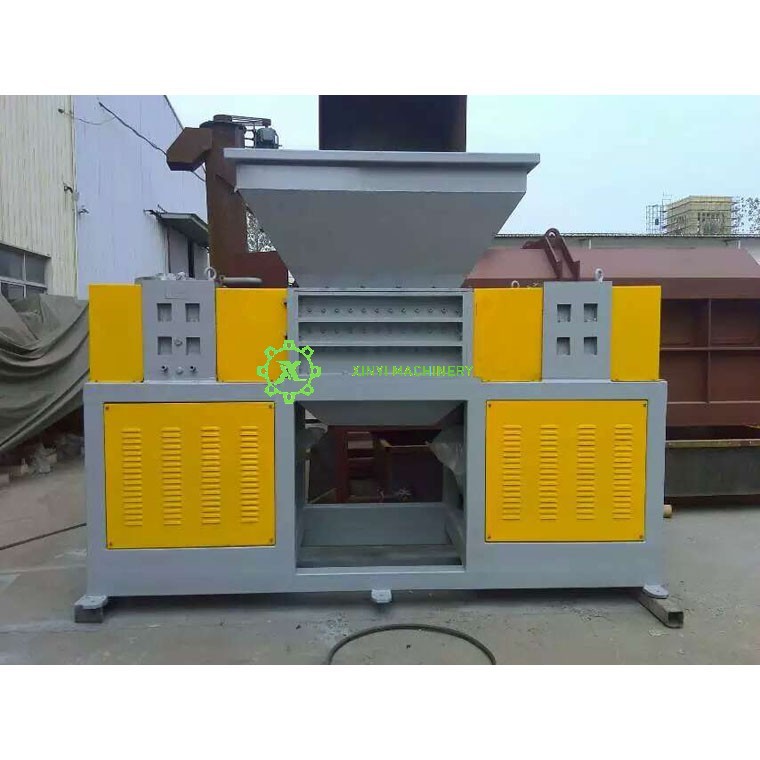
· Plastic Shredder:
o Uses tearing, ripping, and grinding mechanisms to break down plastic into irregular, larger pieces (10–100 mm or more).
o Handles softer, bulkier, or flexible plastics (e.g., films, bags, pipes).
o Output is coarser and may require further processing.
2. Applications
· Crusher: Best for precise size reduction before extrusion, injection molding, or pelletizing.
· Shredder: Used for bulk volume reduction, initial breakdown of large items, or waste preprocessing.
3. Design & Power
· Crusher:
o Higher-speed rotation for fine cutting.
o Often has a screen/mesh to control output size.
· Shredder:
o Lower speed but higher torque for tearing tough materials.
o May have dual-shaft or single-shaft designs for heavy-duty shredding.
4. Common Use Cases
· Crusher: PET bottles, small plastic parts, injection molding scraps.
· Shredder: Plastic films, pipes, drums, electronic waste, mixed plastic waste.
Conclusion
Choose a crusher for fine, controlled granulation and a shredder for initial breakdown of large or tough plastics. Some recycling lines use both—shredding first, then crushing for uniform output.
Last but not least, In some countries, people don’t separate plastic crushers with plastic shredders. They think they are same machines.
the photo of a plastic crusher.
The photo of a shredder.