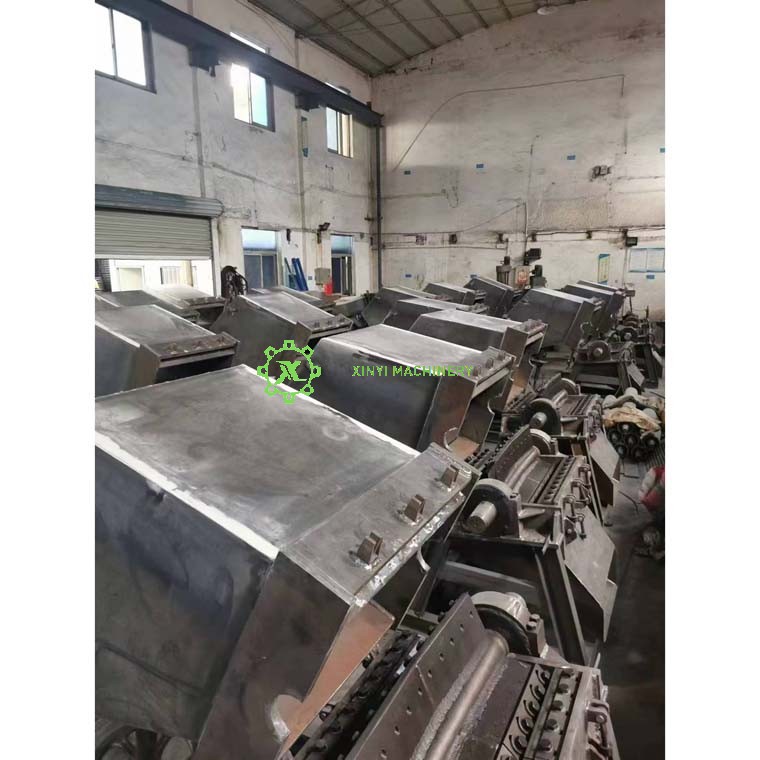
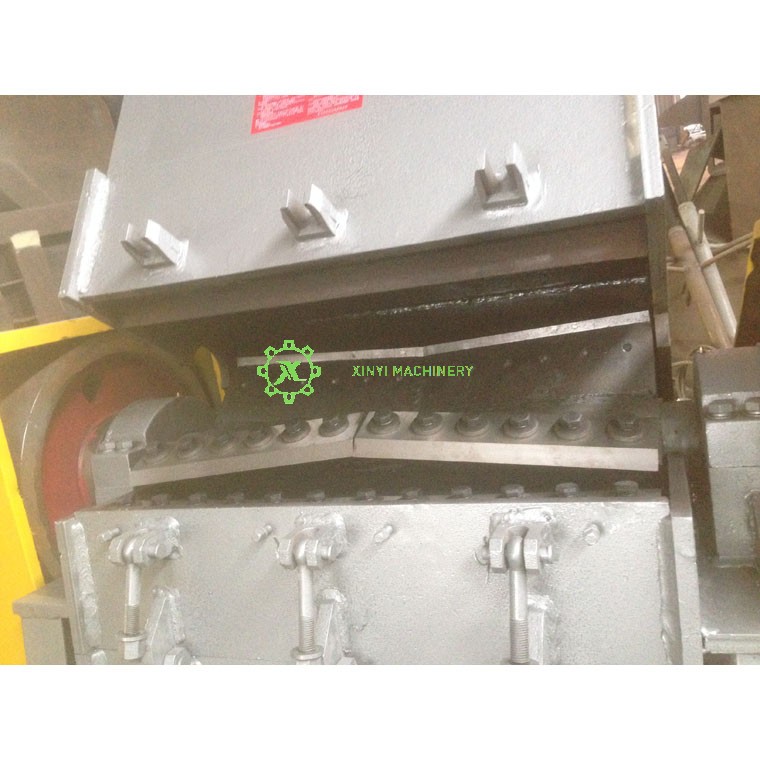
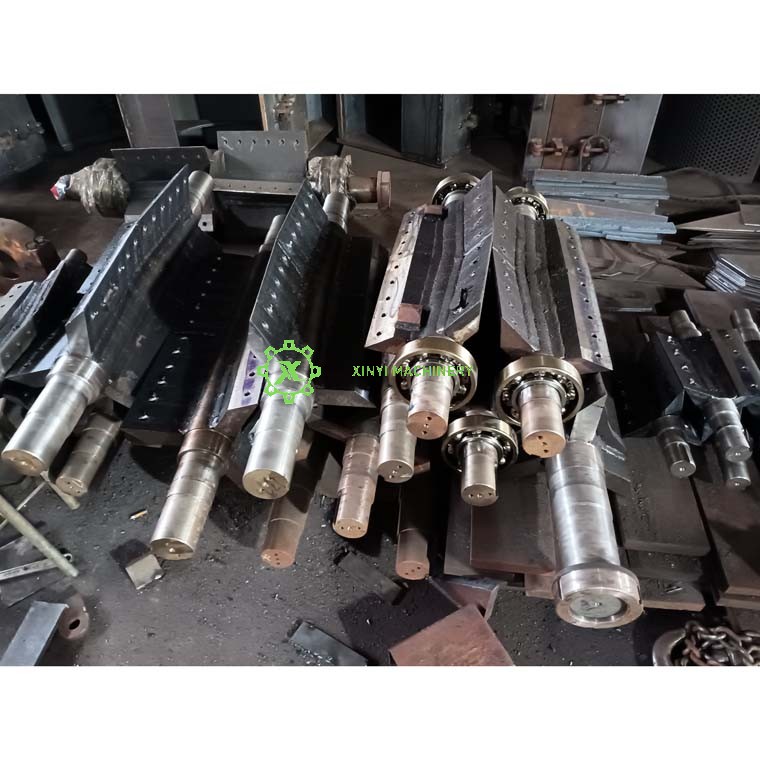
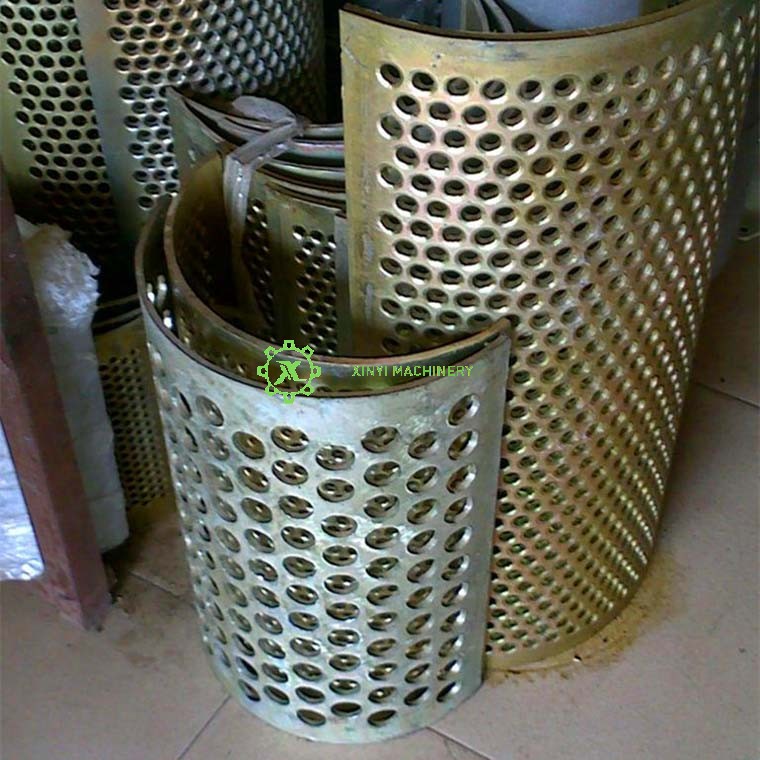
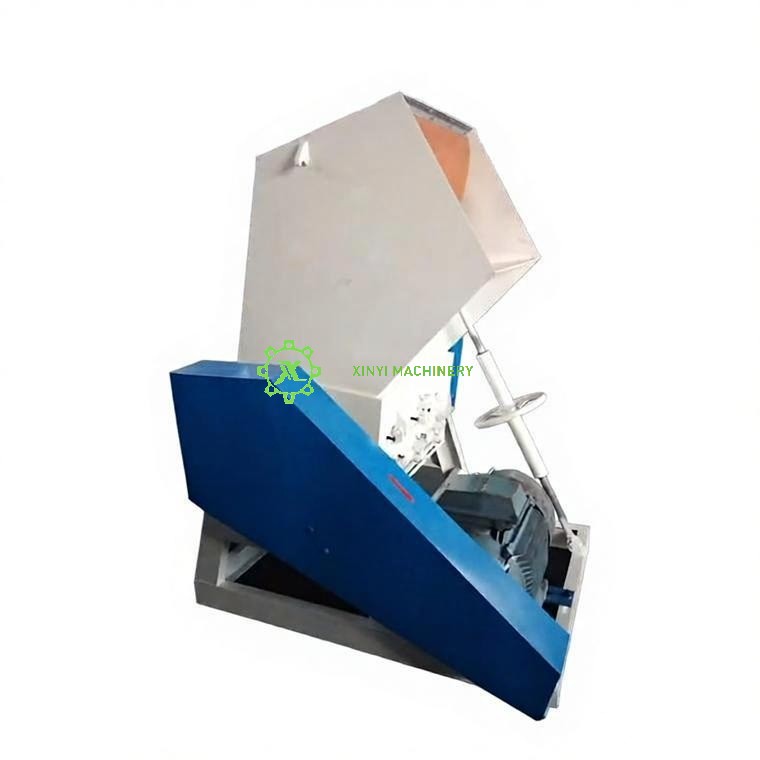
Core Crushing Components:
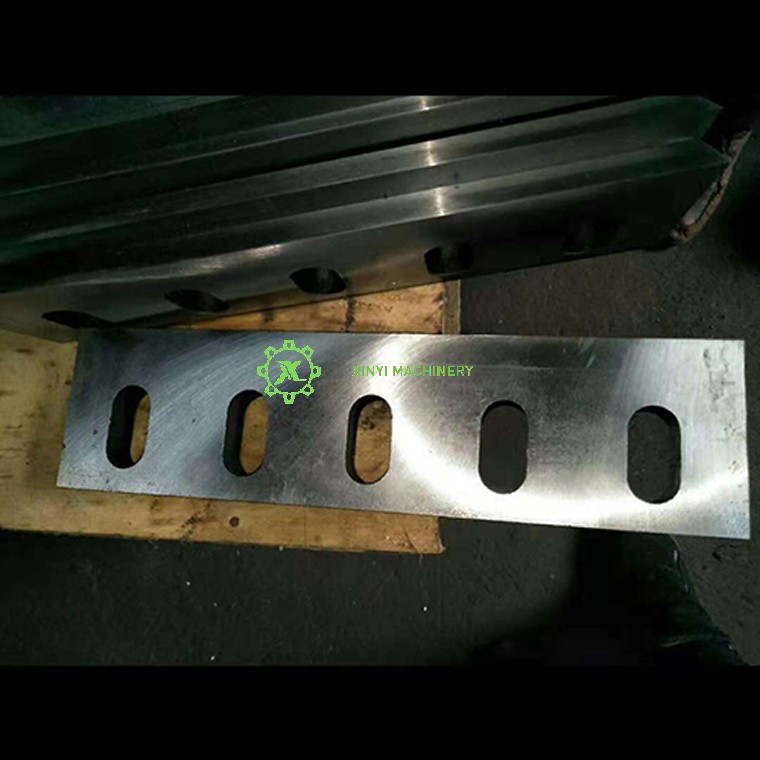
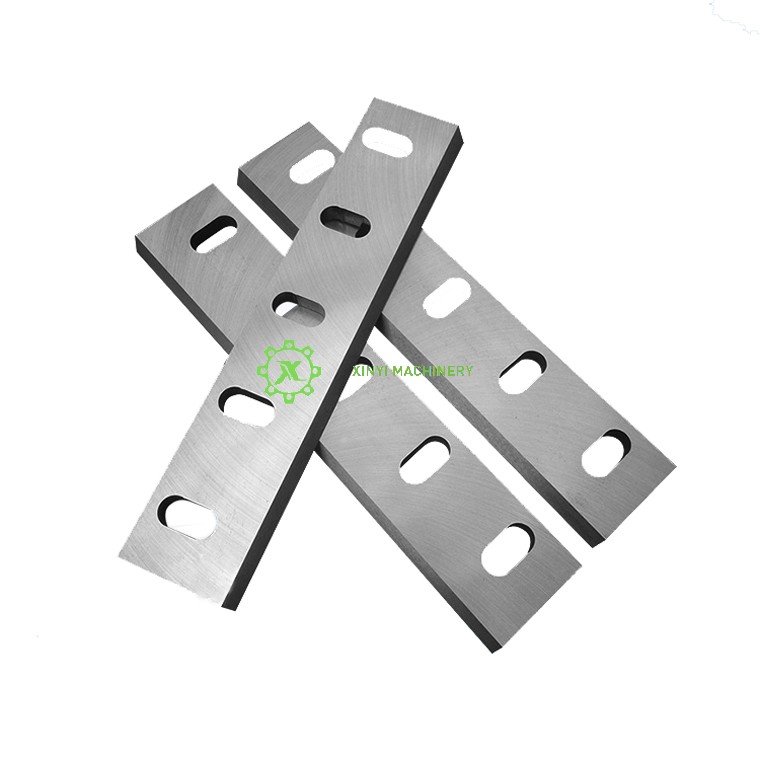
Cutting Blades (Knives):
Rotary Blades (Rotor Blades): Mounted on the rotating rotor shaft. These are the primary cutting elements.
Fixed Blades (Bed Knives/Stator Blades): Securely mounted on the crushing chamber housing opposite the rotary blades. The plastic is sheared between the rotary and fixed blades.
Rotor:
The central rotating shaft assembly that holds the rotary blades. Its design (solid or disc type), diameter, speed, and blade configuration significantly impact crushing efficiency and capacity. Often includes balancing features.
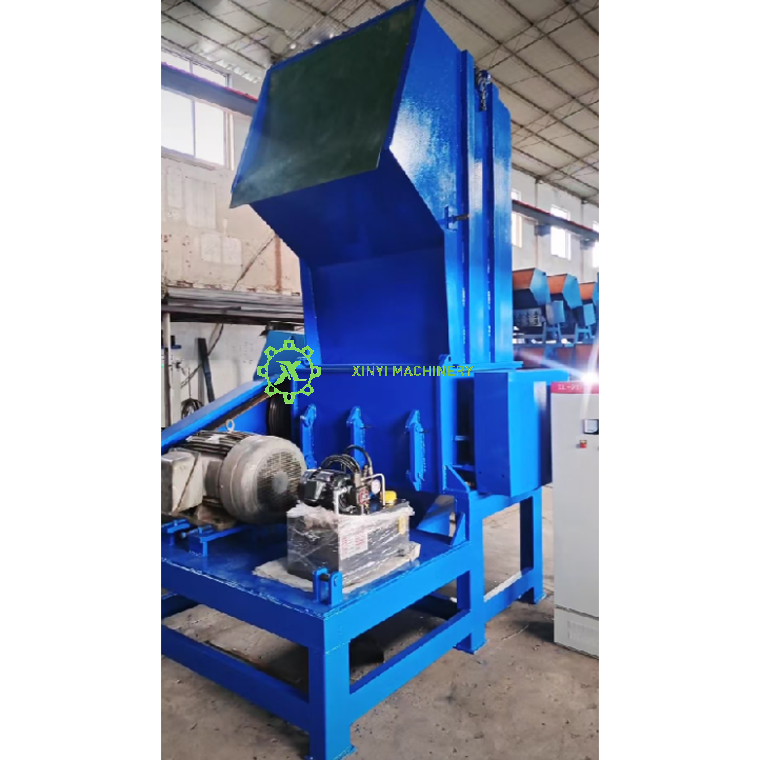
Crushing Chamber (Housing):
The enclosed compartment where the actual shredding occurs. Houses the rotor, fixed blades, and defines the cutting geometry. Designed for strength and often lined with replaceable wear plates.
Screen (Sieve/Grate):
Located at the bottom of the crushing chamber. Determines the final particle size of the crushed plastic. Holes or slots allow particles smaller than the screen opening to pass through, while larger pieces are recycled for further cutting. Screens are interchangeable for different output sizes.
Hopper (Feed Chute):
Upper Hopper: The entry point for plastic material. Guides material into the crushing chamber. Often designed with sloping walls for gravity feed and may include features to prevent material bridging.
Drive & Power Transmission:
Electric Motor:
* Provides the power to drive the rotor. Size (kW/HP) determines the machine's capacity and ability to handle tough materials. Can be mounted directly or via a belt drive.
Transmission System:
* Direct Drive: Motor shaft directly coupled to the rotor shaft (common in smaller units).
* Belt & Pulley Drive: Uses V-belts (or timing belts) and pulleys to transfer power from the motor to the rotor shaft. Allows for speed reduction/increase and absorbs some shock loads.
* Gear Reducer (Less common in standard crushers, more for shredders): Used for very high torque requirements.
Structural & Support Components:
Base Frame:
* The rigid foundation supporting the entire machine (motor, crushing chamber, hopper, etc.). Ensures stability during operation, often with mounting points.
Bearings:
* Heavy-duty bearings support the rotor shaft ends within the crushing chamber housing, allowing smooth high-speed rotation under significant load.
Control & Safety Systems:
Electrical Control Panel:
* Houses motor starters, overload protection, control circuitry (Start/Stop buttons), and often a main circuit breaker.
Auxiliary Components (Often Optional/Integrated):
Dust Extraction Port:
* Connection point for an external dust collection system to remove fines and airborne particles generated during crushing.