A shredder is a machine designed to cut or tear materials into small pieces, strips, or fragments. The most common type is the paper shredder, but shredders exist for various other materials too. Here's a breakdown:
Paper Shredder:
Strip-Cut: Cuts paper into long, thin vertical strips. Least secure, as strips can potentially be reassembled.
Cross-Cut (Confetti-Cut): Cuts paper both vertically and horizontally into small rectangular or diamond-shaped pieces. Much more secure than strip-cut.
Micro-Cut/Particle-Cut: Cuts paper into tiny, confetti-like particles (often 5mm x 5mm or smaller). Offers the highest level of security.
Purpose: Primarily used to destroy confidential or sensitive documents (bills, bank statements, personal letters, business documents) to prevent identity theft, information leaks, or comply with privacy laws.
How it Works: Documents are fed into the shredder (manually or automatically). Inside, rotating blades (cutters) cut the paper.
Cut Types:
Features: Vary by model and include capacity (sheets per pass), security level, bin size, auto-feed, jam prevention, and ability to shred staples, credit cards, CDs/DVDs.
Garden Shredder (Wood Chipper/Shredder):
Purpose: Used to reduce garden waste (branches, twigs, leaves, hedge trimmings) into much smaller chips or mulch.
Benefits: Reduces waste volume significantly, produces useful mulch for composting or garden paths, makes disposal easier.
Types: Often categorized by mechanism - roller shredders (quieter, better for softer material) and blade/turbine shredders (faster, better for woody branches).
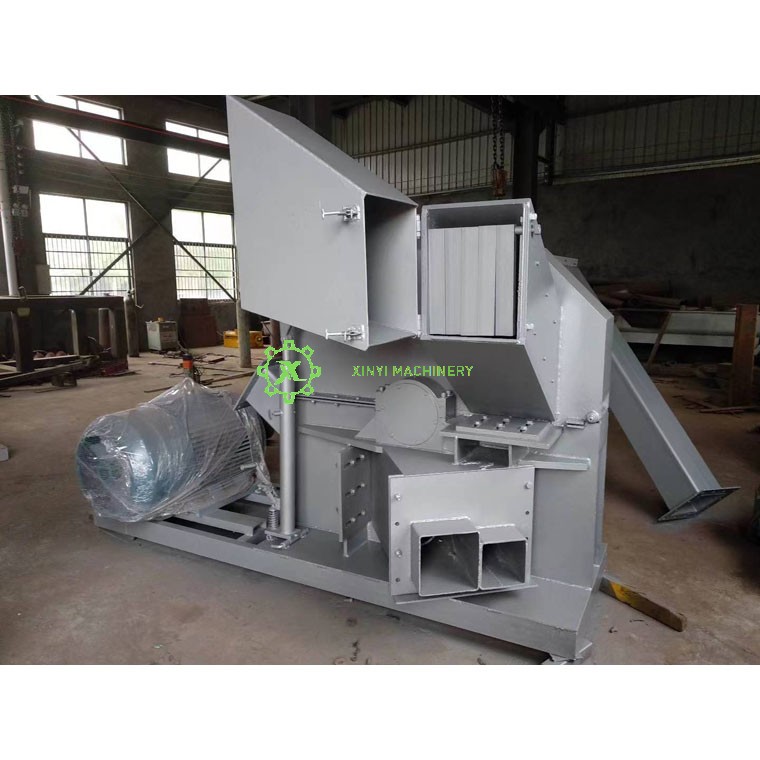
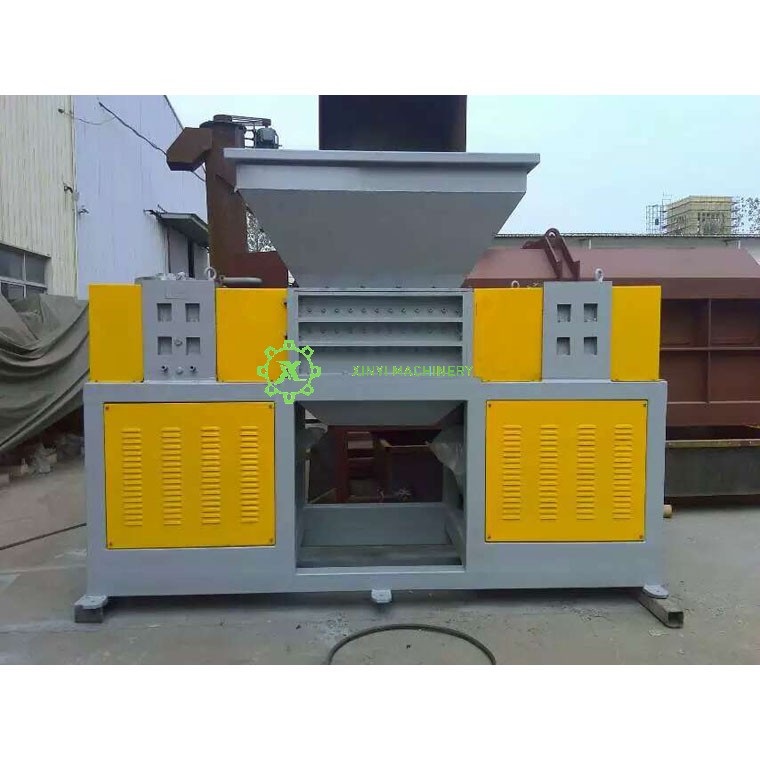
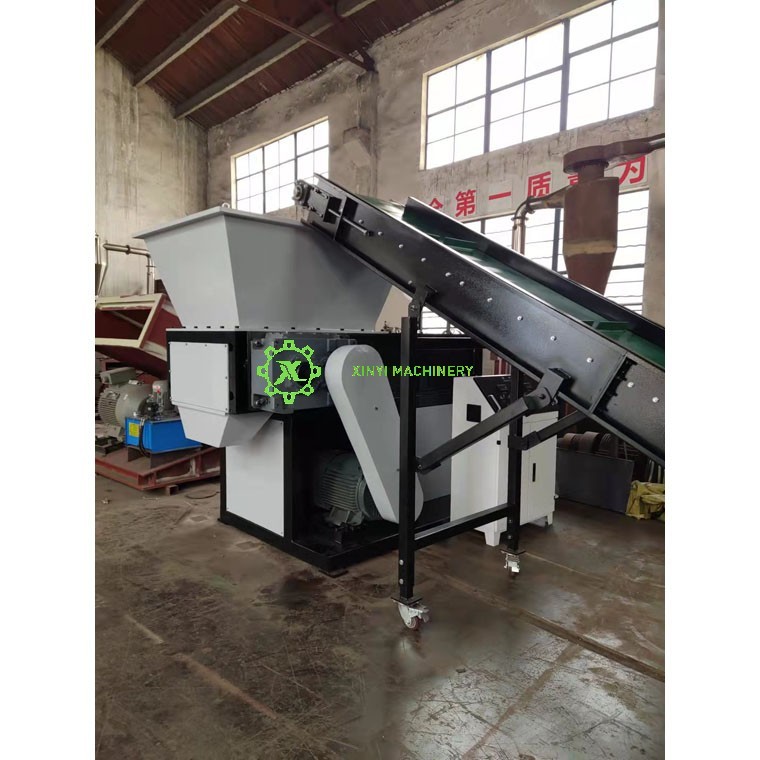
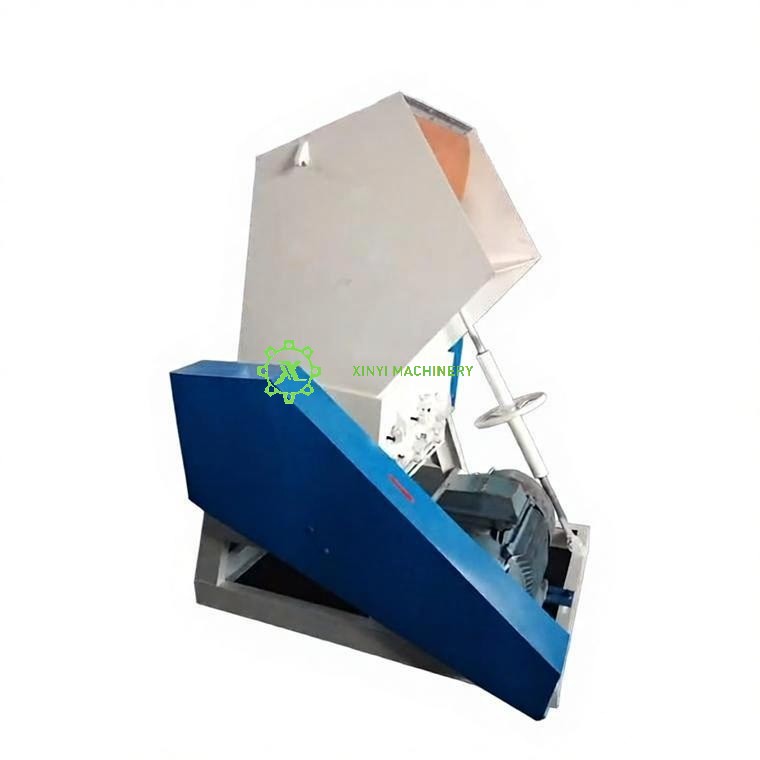
Industrial Shredder:
Purpose: Heavy-duty machines used in recycling facilities, manufacturing, and waste management to shred large volumes of diverse materials.
Materials Shredded: Metal (cars, appliances), plastic, tires, electronic waste (e-waste), textiles, industrial waste, and sometimes even confidential documents at an industrial scale.
Function: Prepares materials for recycling by reducing size, separating components, and destroying sensitive items. Essential for resource recovery.
Other Types:
Food Shredder: While often called "graters" or part of food processors, some devices specifically shred cheese, vegetables, etc.
Tire Shredder: A specific type of industrial shredder for recycling used tires.
Data Shredder: Software that securely deletes digital files by overwriting data (though not a physical machine, it uses the same concept of destroying information).
Key Reasons to Use a Shredder:
Security (Paper): Protect sensitive personal or business information from falling into the wrong hands.
Privacy: Comply with data protection regulations (like GDPR, HIPAA).
Recycling & Waste Reduction (Garden/Industrial): Process materials for easier recycling or composting, reduce landfill volume.
Resource Recovery (Industrial): Break down materials like metal, plastic, and e-waste for reuse in manufacturing.
Convenience (Garden): Manage garden waste efficiently.
In essence, a shredder is any machine that mechanically reduces the size and integrity of a material, whether for security, recycling, waste management, or resource recovery. The most familiar type for everyday use is the paper shredder. In some countries, shredders are also called shredder machines or crushers.